Hi everyone!
TDLR: How to set up an infrared receiver, add/configure a remote and program the keys to control MoodeAudio without using LIRC.
I wanted to control my moodeaudio using a remote control and so far I've been using LIRC so after the last kernel updates it got so messy to set-it up that I just gave up on it. Personally, I'm much happier with this new solution however but please bare in mind that I'm a complete newbie with python and any help to improve what I'm sharing below is much appreciated. I might have forgotten to document something on the way, if so please let me know and I'll update the original thread.
Credits: This is based mainly on Lime-Parallelogram work and she goes through it in detail in this video.
My hardware:
Raspberry pi 4
A generic remote control
IR sensor TL1838
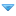
- 3 - Left - Out - GPIO 17 or pin 11 (you can use other GPIO but make sure to check the pin number)
- 2 - Middle - GND - pin 9
- 1 - Right - VCC 3.3v - pin 1
1 - Connect the sensor to the raspberry
![[Image: 2021-02-23_21_45_27-gpio_-_raspberry_pi_...tation.png]](http://192.168.0.195:2370/2021-02-23_21_45_27-gpio_-_raspberry_pi_documentation.png)
2 - Set up the gpio and install dependencies
Edit /boot/config.txt
add
Reboot
3. Decode the remote(s) you wanna use
get the files and run the program
You'll be asked to set the sensor pin. use the pin number (not GPIO number) in this case pin 11. Add a name for the remote (anything you want) and start adding keys.
Once you're done there will be a txt file with the remote name. open this file (e.g. nano remote.txt) and copy those values to some notepad.
4. Prepare the python script
download the script from Lime-Parallelogram
edit the script
firstly add the following line 'import subprocess' at the top of the script
next, replace the list in the variables Buttons and ButtonsNames for the HEX codes and names you set up in your remote on step 3. In my case my remote has 5 buttons so I got in my txt;
therefore my variables in the script will become
you can save it and confirm working by running it
when pressing the buttons you should get the button name output.
4. Make the script control MPC
going back to our script (nano ir-scrypt.py) look for this code right in the end
while True:
just after this, we can add some conditions to control MPC in moodeaudio. Probably there are much better ways how to tackle this. I managed to make it work by using conditions. Here's my example:
If you want more buttons just copy the elif and the line after it.
List of MPC commands you can change the subprocess.call as you see fit.
You can test and run it again 'python ir-scrypt.py'.
4. Make the scrypt run on boot
You can replace my_python for name:
If your script is at the same location as above, when it was created then paste the code below otherwise adjust the location:
then run
you can reboot and the service should start.
I hope it works as well for you as it did for me
TDLR: How to set up an infrared receiver, add/configure a remote and program the keys to control MoodeAudio without using LIRC.
I wanted to control my moodeaudio using a remote control and so far I've been using LIRC so after the last kernel updates it got so messy to set-it up that I just gave up on it. Personally, I'm much happier with this new solution however but please bare in mind that I'm a complete newbie with python and any help to improve what I'm sharing below is much appreciated. I might have forgotten to document something on the way, if so please let me know and I'll update the original thread.
Credits: This is based mainly on Lime-Parallelogram work and she goes through it in detail in this video.
My hardware:
Raspberry pi 4
A generic remote control
IR sensor TL1838
- 3 - Left - Out - GPIO 17 or pin 11 (you can use other GPIO but make sure to check the pin number)
- 2 - Middle - GND - pin 9
- 1 - Right - VCC 3.3v - pin 1
1 - Connect the sensor to the raspberry
![[Image: 2021-02-23_21_45_27-gpio_-_raspberry_pi_...tation.png]](http://192.168.0.195:2370/2021-02-23_21_45_27-gpio_-_raspberry_pi_documentation.png)
2 - Set up the gpio and install dependencies
Code:
sudo apt install python3-gpiozeroEdit /boot/config.txt
Code:
sudo nano /boot/config.txtadd
Code:
dtoverlay=gpio-ir,gpio_pin=17Reboot
3. Decode the remote(s) you wanna use
get the files and run the program
Code:
git clone https://github.com/Lime-Parallelogram/IR-Code-Decoder--
cd IR-Code-Decoder--
python CLI.pyYou'll be asked to set the sensor pin. use the pin number (not GPIO number) in this case pin 11. Add a name for the remote (anything you want) and start adding keys.
Once you're done there will be a txt file with the remote name. open this file (e.g. nano remote.txt) and copy those values to some notepad.
4. Prepare the python script
download the script from Lime-Parallelogram
Code:
cd ~
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Lime-Parallelogram/IR-Code-Referencer/10e7598d0e860675cd3ea7972661e9e9aa3e5a3c/Final-From-Video.py
mv Final-From-Video.py ir-scrypt.pyedit the script
Code:
nano ir-scrypt.pyfirstly add the following line 'import subprocess' at the top of the script
Code:
#Imports modules
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from datetime import datetime
import subprocessnext, replace the list in the variables Buttons and ButtonsNames for the HEX codes and names you set up in your remote on step 3. In my case my remote has 5 buttons so I got in my txt;
Quote:Button Code - enter: 0x3482c20dfL
Button Code - up: 0x3482c40bfL
Button Code - left: 0x3482cc03fL
Button Code - right: 0x3482ca05fL
Button Code - down: 0x3482c609fL
therefore my variables in the script will become
Code:
Buttons = ["0x3482c20dfL","0x3482c40bfL","0x3482cc03fL","0x3482ca05fL","0x3482c609fL"]
ButtonsNames = ["enter","up","left","right","down"]you can save it and confirm working by running it
Code:
python ir-scrypt.pywhen pressing the buttons you should get the button name output.
4. Make the script control MPC
going back to our script (nano ir-scrypt.py) look for this code right in the end
while True:
Code:
inData = convertHex(getBinary()) #Runs subs to get incomming hex value
for button in range(len(Buttons)):#Runs through every value in list
if hex(Buttons[button]) == inData: #Checks this against incommingjust after this, we can add some conditions to control MPC in moodeaudio. Probably there are much better ways how to tackle this. I managed to make it work by using conditions. Here's my example:
Code:
while True:
inData = convertHex(getBinary()) #Runs subs to get incomming hex value
for button in range(len(Buttons)):#Runs through every value in list
if hex(Buttons[button]) == inData: #Checks this against incomming
if ButtonsNames[button] == "enter":
subprocess.call(["mpc", "toggle"])
elif ButtonsNames[button] == "up":
subprocess.call(["mpc", "prev"])
elif ButtonsNames[button] == "down":
subprocess.call(["mpc", "next"])
elif ButtonsNames[button] == "left":
subprocess.call(["mpc", "seek","-5%"])
elif ButtonsNames[button] == "right":
subprocess.call(["mpc", "seek","+5%"])If you want more buttons just copy the elif and the line after it.
List of MPC commands you can change the subprocess.call as you see fit.
You can test and run it again 'python ir-scrypt.py'.
4. Make the scrypt run on boot
You can replace my_python for name:
Code:
sudo nano /lib/systemd/system/my_python.serviceIf your script is at the same location as above, when it was created then paste the code below otherwise adjust the location:
Code:
[Unit]
Description=My python script for OLED, buttons and remote control
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python /home/pi/ir-scrypt.py
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetthen run
Code:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable my_python.service
systemctl status my_python.serviceyou can reboot and the service should start.
I hope it works as well for you as it did for me